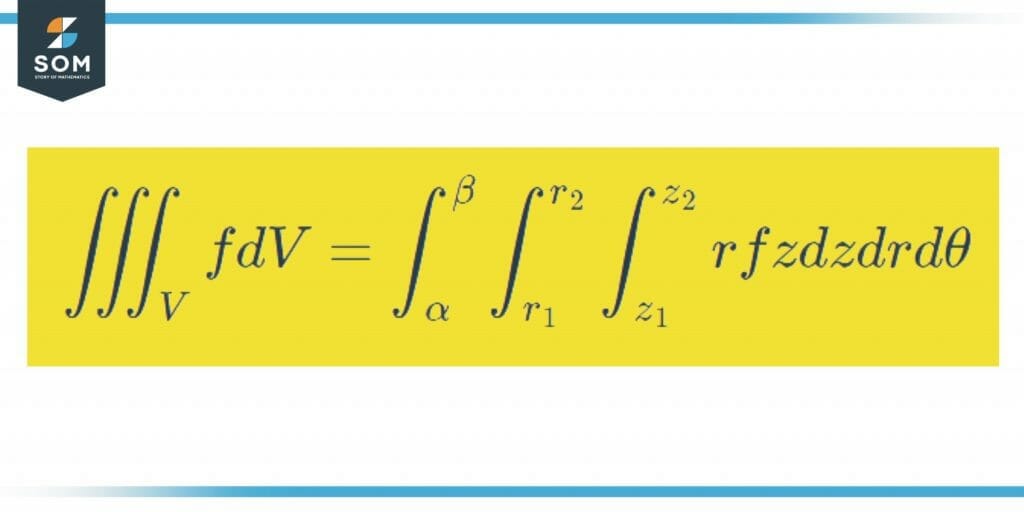
Cylindrical Coordinates Integral Calculator + Online Solver with Free Steps
Using cylindrical coordinates can greatly simplify a triple integral when the region you are integrating over has some kind of rotational symmetry about the z -axis. The one rule When performing double integrals in polar coordinates, the one key thing to remember is how to expand the tiny unit of area d A in terms of d r and d θ
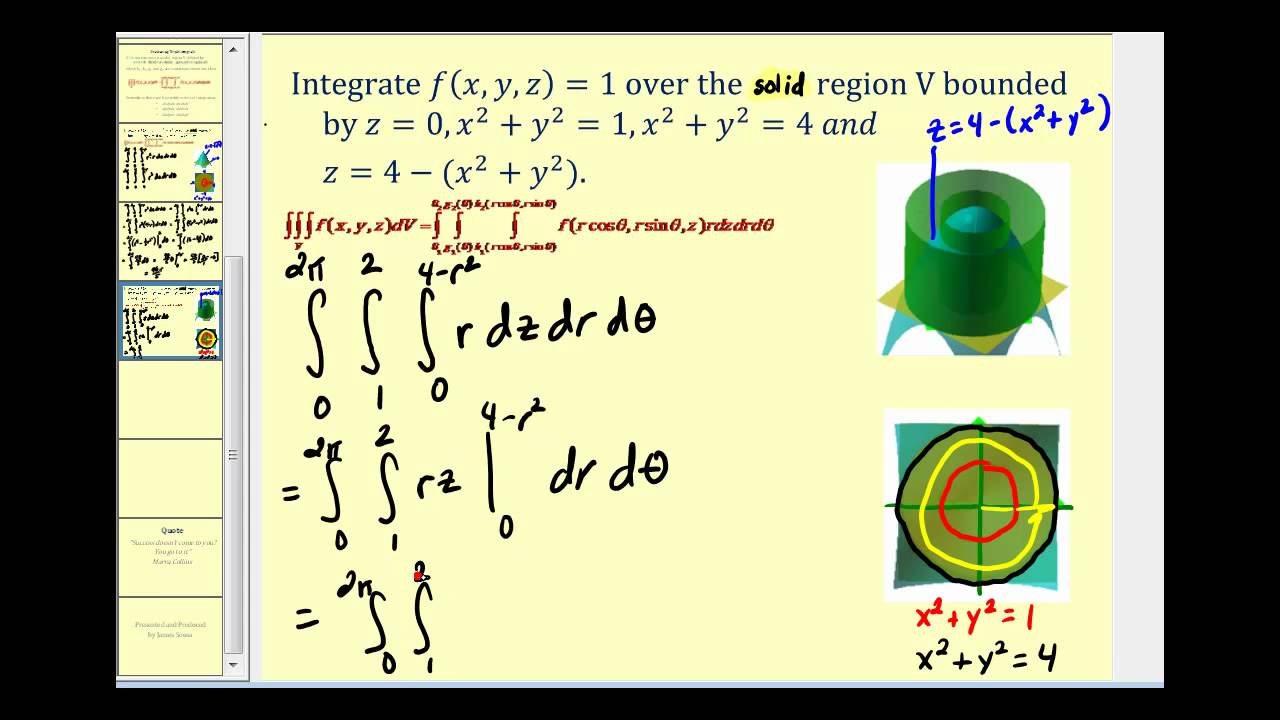
Triple Integrals Using Cylindrical Coordinates YouTube
Integration in Cylindrical Coordinates: To perform triple integrals in cylindrical coordinates, and to switch from cylindrical coordinates to Cartesian coordinates, you use: x= rcos ; y= rsin ; z= z; and dV = dzdA= rdzdrd : Example 3.6.1. Find the volume of the solid region Swhich is above the half-cone

4c. Volume of a cone as a triple integral in cylindrical coordinates
Solves a triple integral with cylindrical coordinates Send feedback | Visit Wolfram|Alpha Get the free "Triple Integral - Cylindrical" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle. Find more Mathematics widgets in Wolfram|Alpha.

Lesson 2 Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates (Calculus 3
Figure 15.7.3: Setting up a triple integral in cylindrical coordinates over a cylindrical region. Solution. First, identify that the equation for the sphere is r2 + z2 = 16. We can see that the limits for z are from 0 to z = √16 − r2. Then the limits for r are from 0 to r = 2sinθ.

Rewrite Triple Integrals Using Cylindrical Coordinates YouTube
We are integrating \(z\) first in the integral set up to use Cartesian coordinates and so we'll integrate that first in the integral set up to use cylindrical coordinates as well. It is easy to convert the \(z\) limits to cylindrical coordinates as follows. \[{r^2} - 11 \le z \le 9 - 3{r^2}\] Show Step 3

Triple Integrals Using Cylindrical Coordinates 2 Vector Calculus
With cylindrical coordinates (r, θ, z), by r = c, θ = α, and z = m, where c, α, and m are constants, we mean an unbounded vertical cylinder with the z -axis as its radial axis; a plane making a constant angle α with the xy -plane; and an unbounded horizontal plane parallel to the xy -plane, respectively.

SOLUTION 6 triple integrals in cylindrical and spherical coordinates
By adding the z-axis, the circle has a height of z, which gives it the shape of a cylinder, hence the name cylindrical coordinates. As seen in Double Integrals in Polar Form, when converting a double integral from Cartesian to polar coordinates, the \(dA\) term, \(dx\,dy\) in Cartesian gets converted to its polar equivilent.
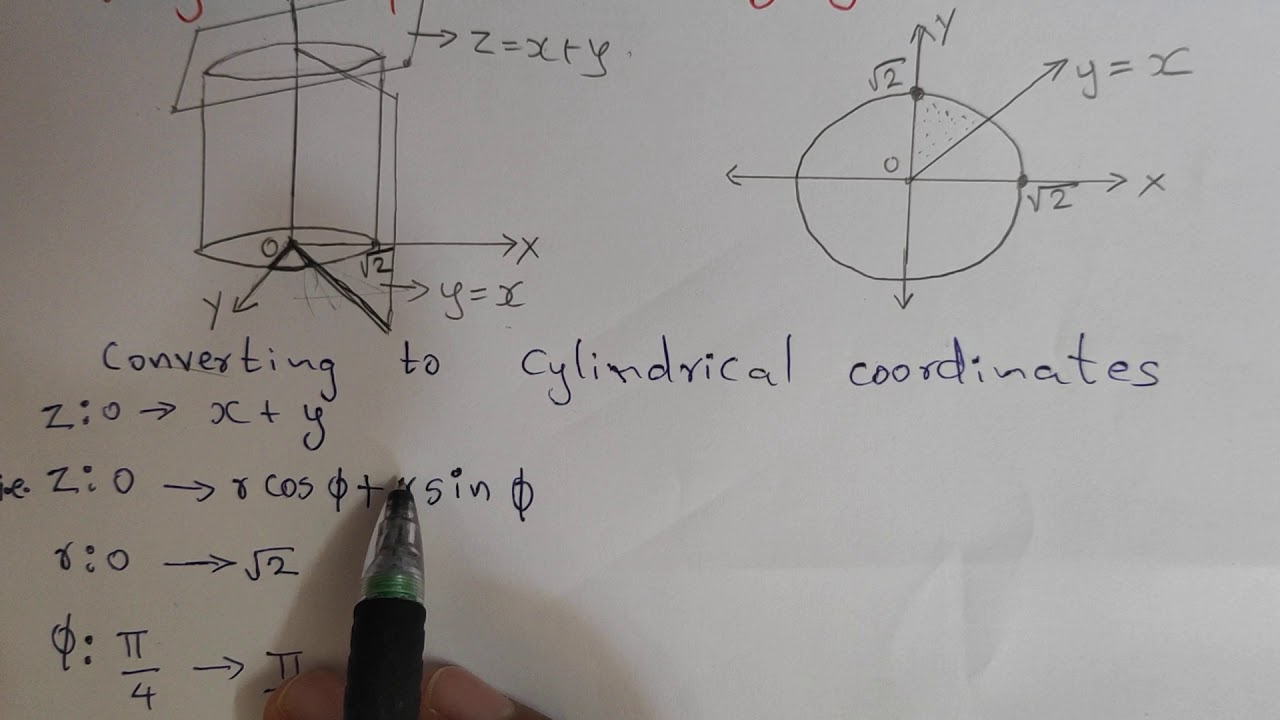
Triple Integrals Cylindrical coordinates YouTube
0,0. Δr. rΔθ. Figure 15.2.1. A cylindrical coordinates "grid''. Example 15.2.1 Find the volume under z = √4 − r2 above the quarter circle bounded by the two axes and the circle x2 + y2 = 4 in the first quadrant. In terms of r and θ, this region is described by the restrictions 0 ≤ r ≤ 2 and 0 ≤ θ ≤ π / 2, so we have ∫π / 2.
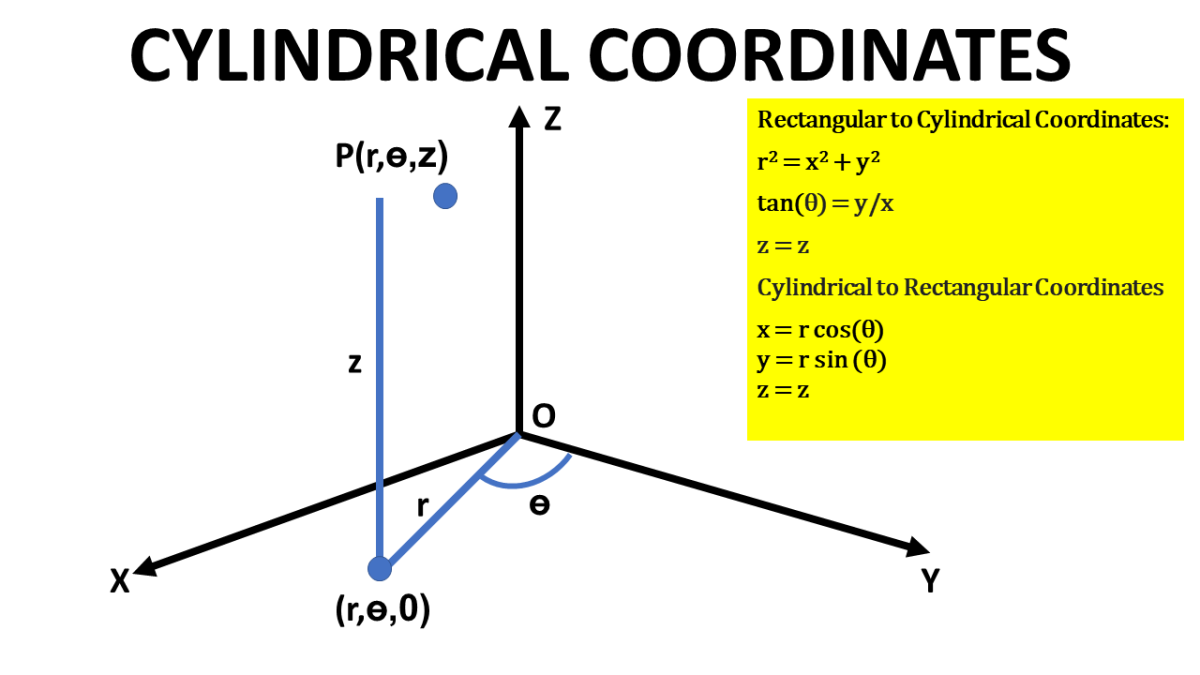
Cylindrical Coordinates Rectangular to Cylindrical Coordinates
Integration in cylindrical coordinates is a simple extension of polar coordinates from two to three dimensions. This coordinate system works best when integrating cylinders or cylindrical-like objects. As with spherical coordinates, cylindrical coordinates benefit from lack of dependency between the variables, which allows for easy factoring. Steps

Triple Integral and Volume Using Cylindrical Coordinates YouTube
1. Evaluate the triple integral in cylindrical coordinates: f(x; y; z) = sin(x2 + y2), W is the solid cylinder with height 4 with base of radius 1 centered on the z-axis at z = 1. Spherical Coordinates The spherical coordinates of a point (x; y; z) in 3 R are the analog of polar coordinates in R 2.

13.7 Integration in Cylindrical Coordinates, Part 2 YouTube
3. Evaluate ∭ E zdV ∭ E z d V where E E is the region between the two planes x+y +z = 2 x + y + z = 2 and x = 0 x = 0 and inside the cylinder y2+z2 = 1 y 2 + z 2 = 1. Show All Steps Hide All Steps. Start Solution.

Converting triple integrals to cylindrical coordinates (KristaKingMath
Answer. Example : Finding a Volume with Triple Integrals in Two Ways. Let E be the region bounded below by the -plane, above by the sphere , and on the sides by the cylinder. (Figure 15.5.5). Set up a triple integral in cylindrical coordinates to find the volume of the region using the following orders of.
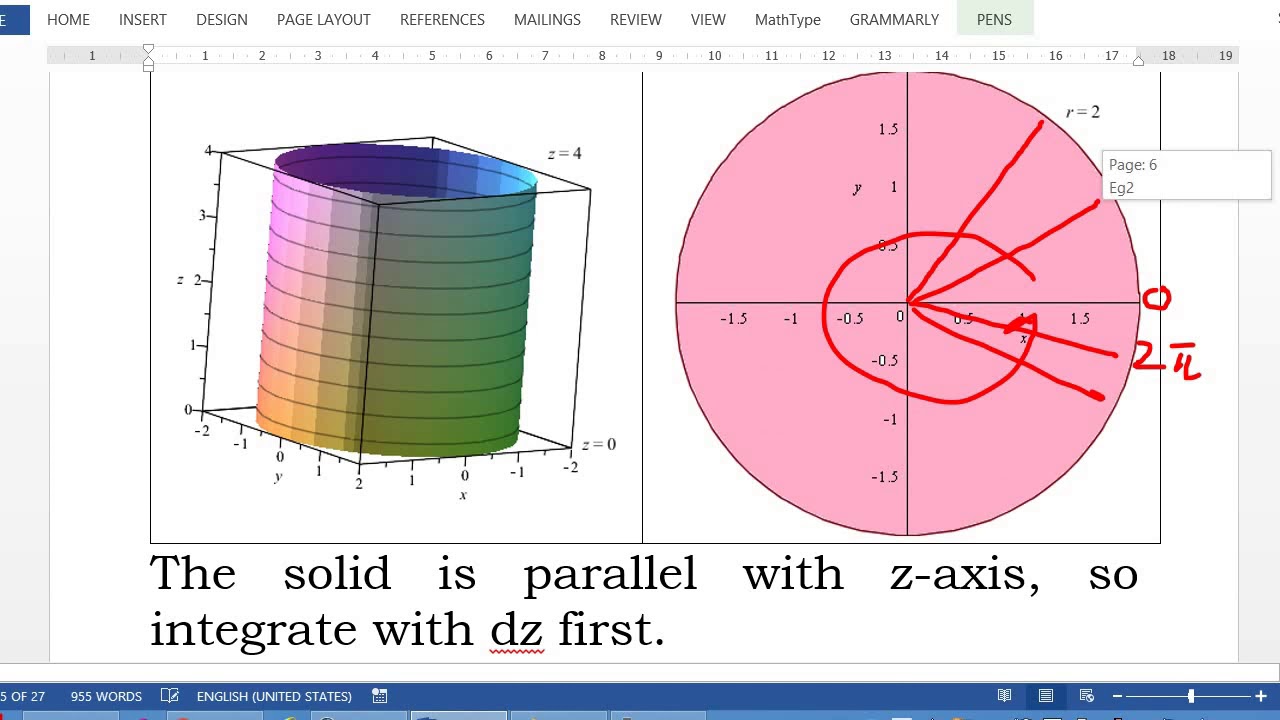
Triple Integral by cylindrical coordinates YouTube
Definition 3.6.1. Cylindrical coordinates are denoted 2 , r, θ and z and are defined by. the distance from to the distance from to the -axis the angle between the positive axis and the line joining to the signed distance from to the -plane r = the distance from ( x, y, 0) to ( 0, 0, 0) = the distance from ( x, y, z) to the z -axis θ = the.

[Math] Change the order of integration in Spherical coordinate and
Definition. Cylindrical coordinates represent a point P in space by the ordered triple (r, θ, z) where r and θ are the polar coordinates for the vertical projection of P onto the xy-plane. z is the rectangular vertical coordinate of P . z P (r, θ, z) b b y x

Video3234 Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates Practice
In terms of cylindrical coordinates a triple integral is, ∭ E f (x,y,z) dV = ∫ β α ∫ h2(θ) h1(θ) ∫ u2(rcosθ,rsinθ) u1(rcosθ,rsinθ) rf (rcosθ,rsinθ,z) dzdrdθ ∭ E f ( x, y, z) d V = ∫ α β ∫ h 1 ( θ) h 2 ( θ) ∫ u 1 ( r cos θ, r sin θ) u 2 ( r cos θ, r sin θ) r f ( r cos θ, r sin θ, z) d z d r d θ
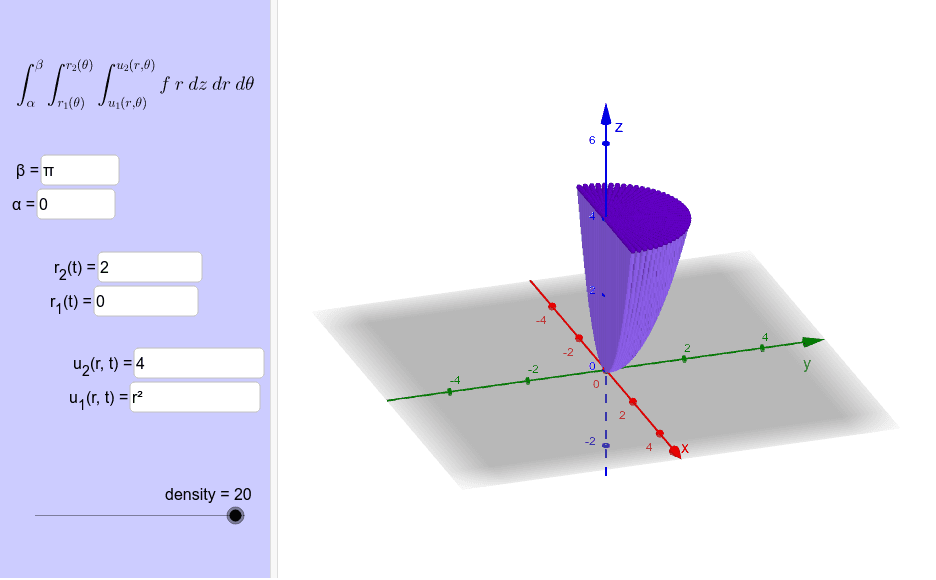
Triple Integral in Cylindrical Coordinates Visualizer GeoGebra
Integration in Cylindrical Coordinates. Triple integrals can often be more readily evaluated by using cylindrical coordinates instead of rectangular coordinates. Some common equations of surfaces in rectangular coordinates along with corresponding equations in cylindrical coordinates are listed in Table 5.1. These equations will become handy as.